The revolutionary R6 Cycle
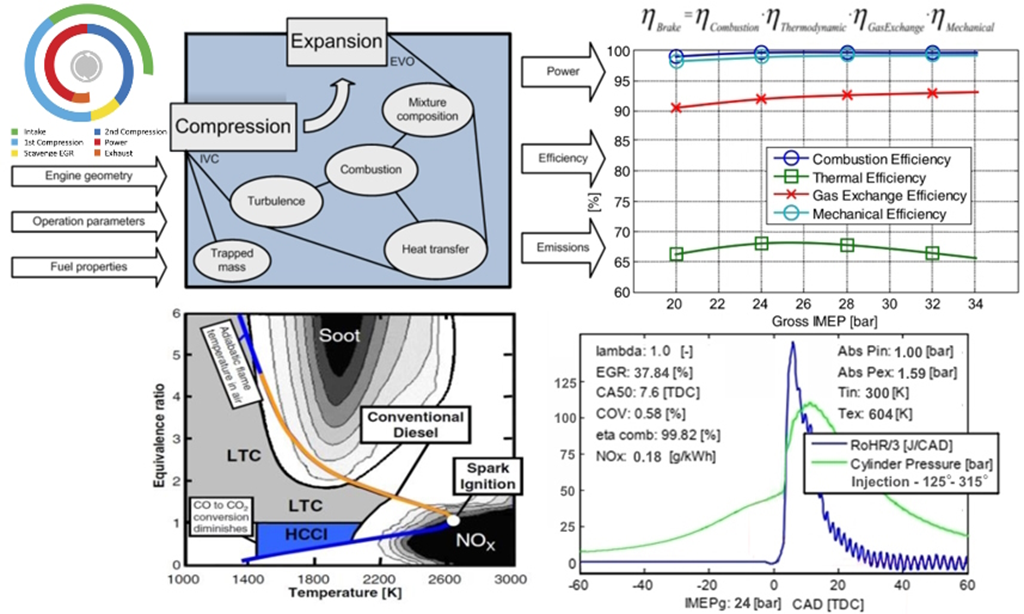
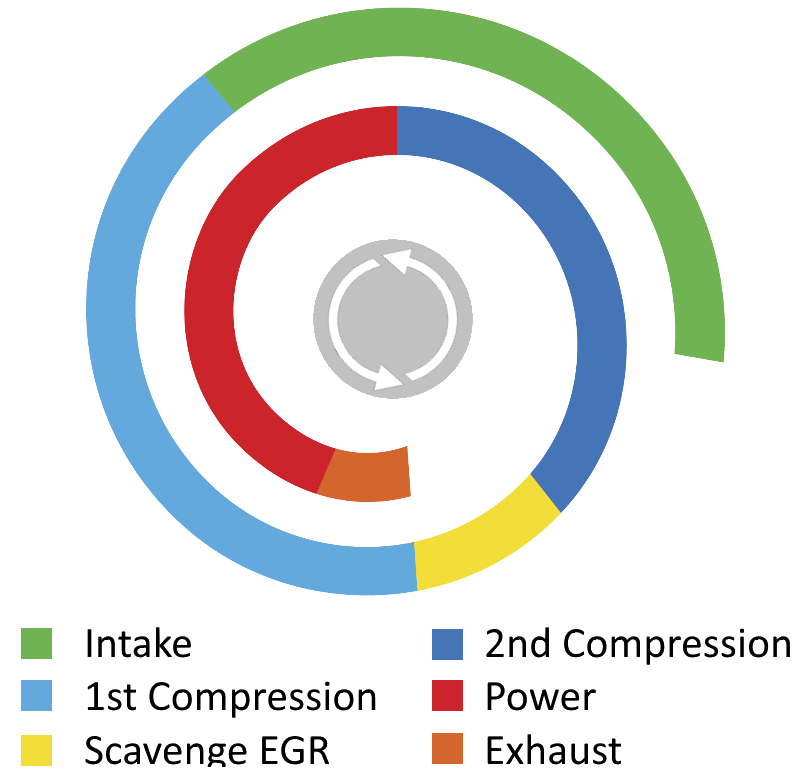
The R6 engine is predicted to be a net zero engine for the 21st Century because its revolutionary rotary architecture and 6-phase thermodynamic cycle (patent EP3765711, 2022) eliminates the problem of engine knock (detonation) and enables high load homogenous charge compression ignition (HCCI) or Hydrogen combustion with >50% brake thermal efficiency and <0.2g/kWh NOx emissions without aftertreatment. Its 6-phase thermodynamic cycle completes in three pairs of phases in each rotation of the shaft: (1) power/ 1st compression, (2) exhaust/ scavenge-EGR, (3) 2nd compression/ intake. The illustration below shows the key stages in the 6-phase cycle.
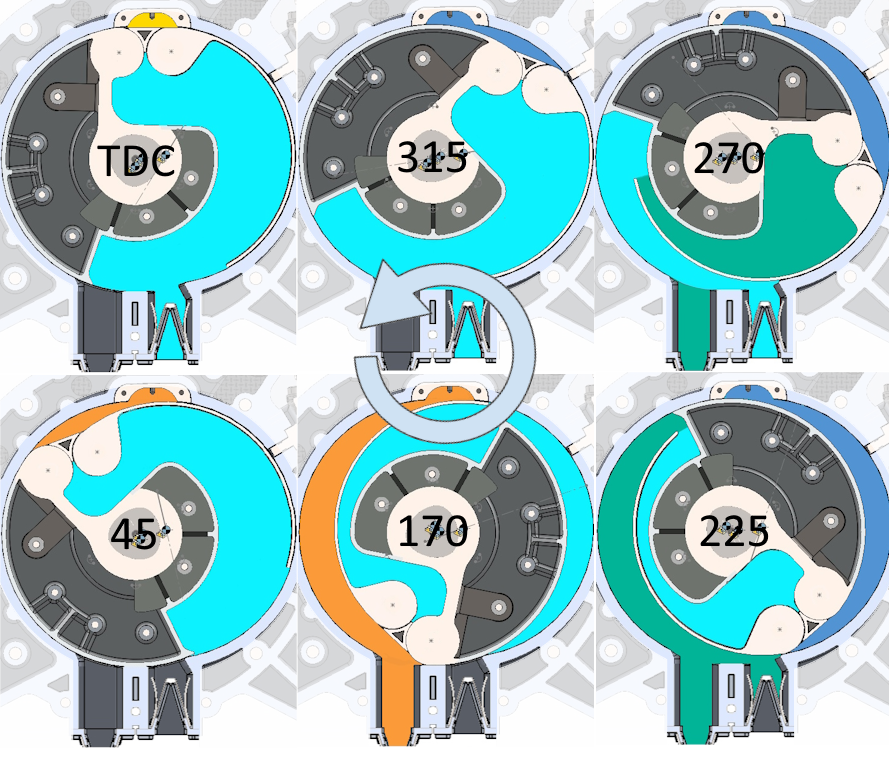
R6 6 Phase Cycle
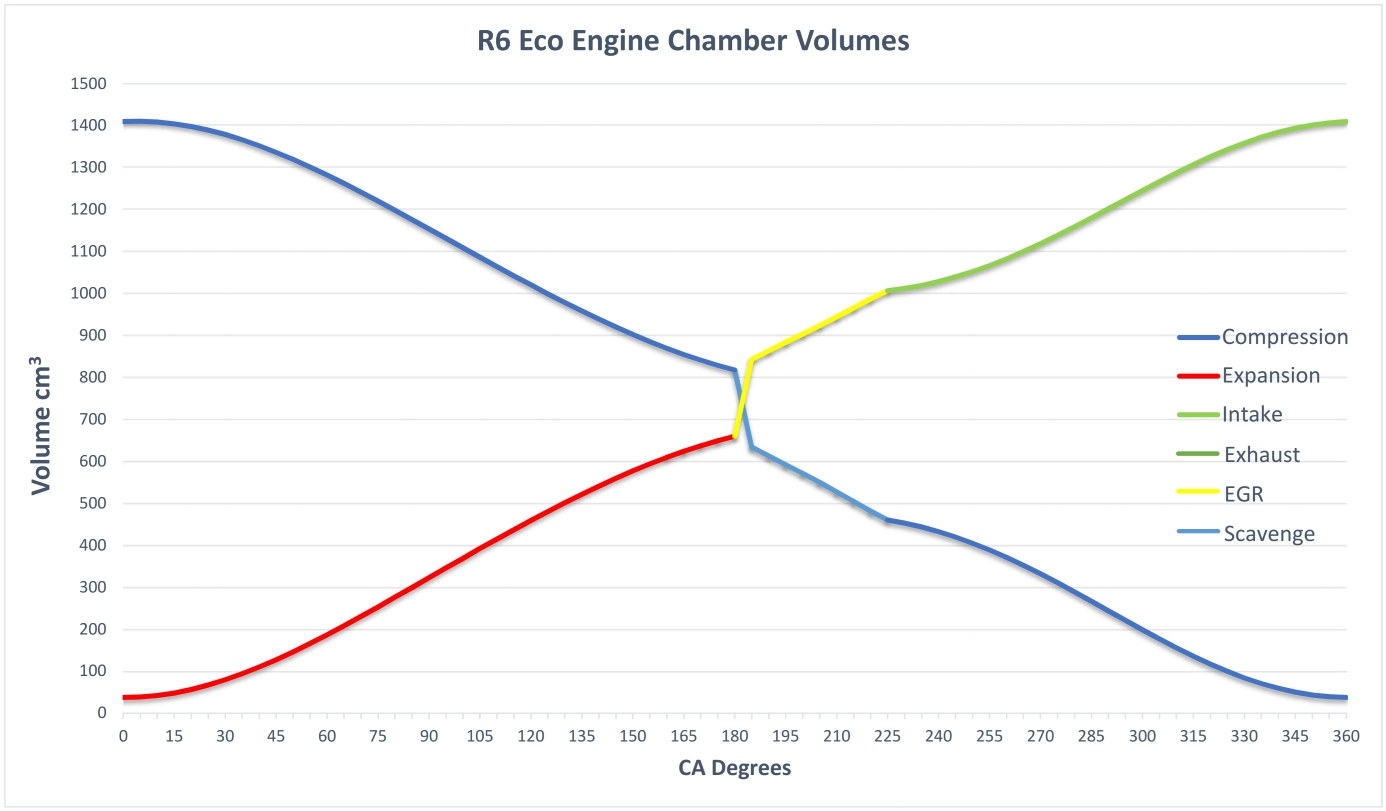
The graph below illustrates the R6 cycle chamber volumes across 360o of rotation.
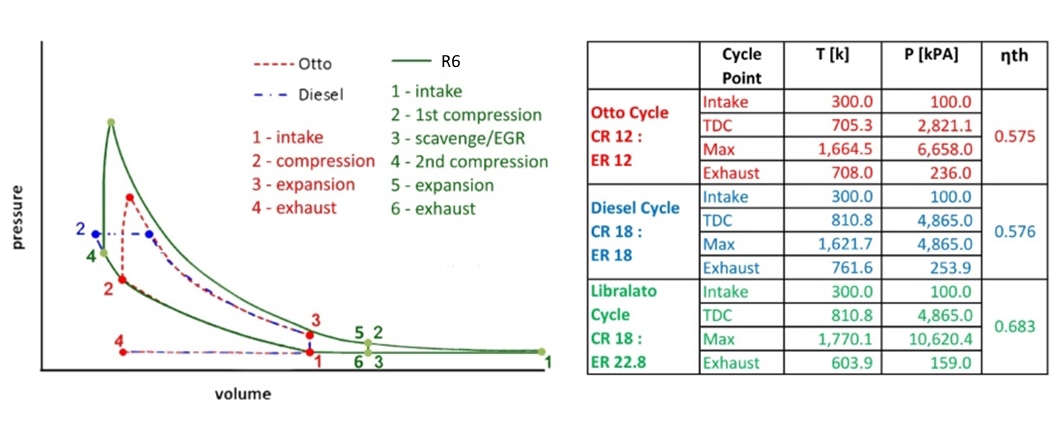
The graph below show a comparison between the R6 cycle and the Otto and Diesel cycles.
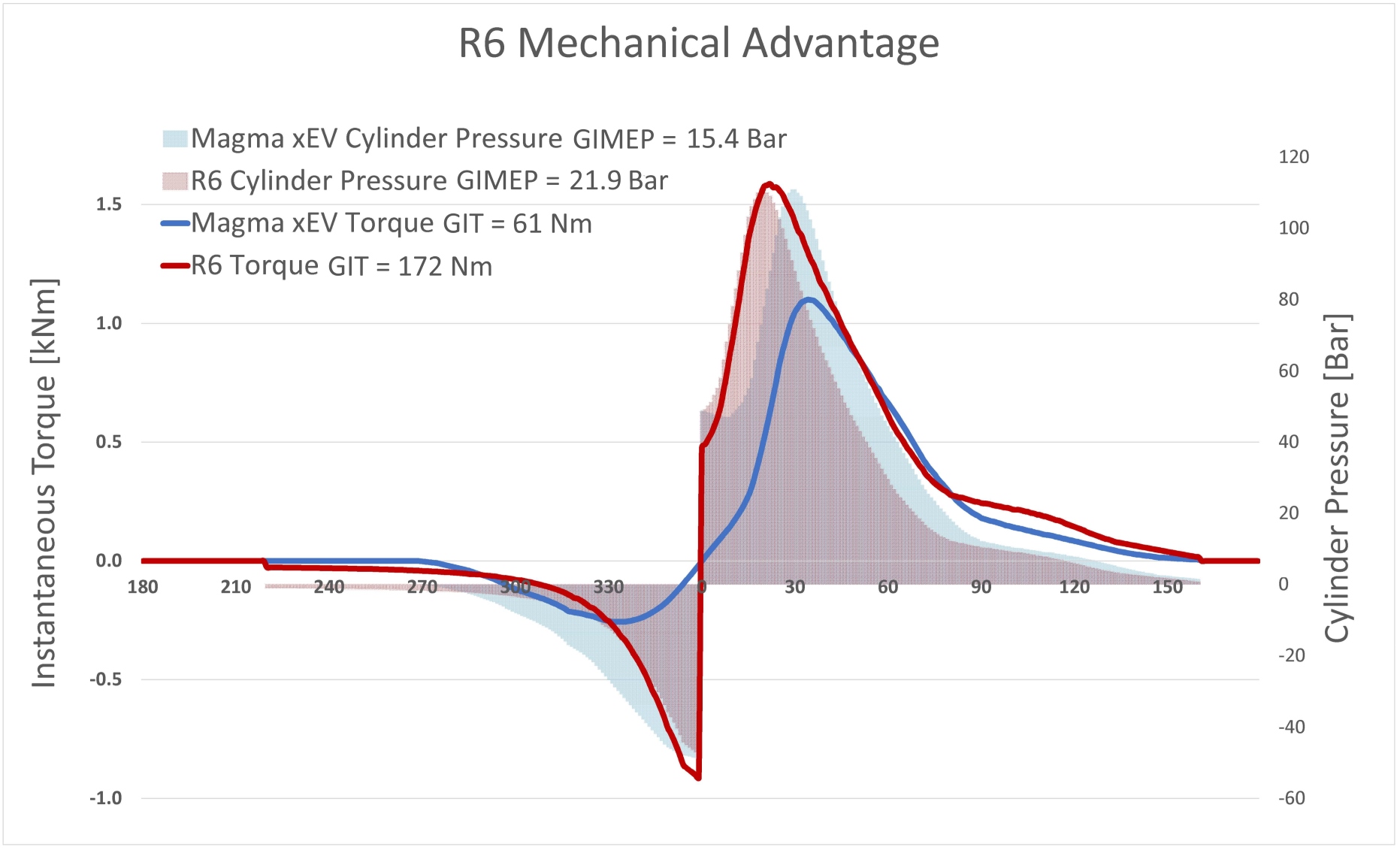
The graph below shows the mechanical advantage of R6 rotary architecture in terms of the torque generated from the same pressure at top dead centre.
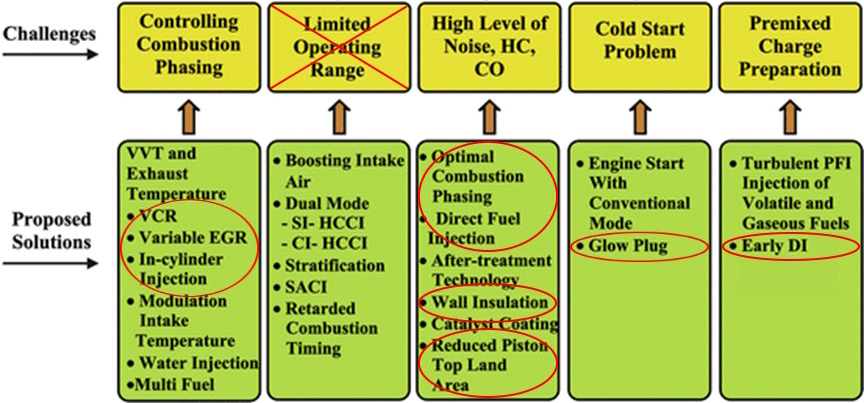
The illustration below shows how R6 engine can utilise HCCI combustion in a way that conventional engines cannot.
The charts below show the modelling methodology and assumptions made based on the engine architecture and 6-phase cycle.